Introduction:
Muscles and joint pain are common complaints that can significantly affect one's quality of life. Whether it's a result of injury, overuse, or an underlying medical condition, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing and alleviating pain effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of muscles and joint pain, exploring its various causes, symptoms, and evidence-based treatment strategies.
Pain o soma 500mg It seems to be an attractive option for relieving nerve-related discomfort. Nevertheless, there are significant concerns over the medication's efficacy and safety. muscular relaxants, such as Pain O Soma and others, have long been prescribed to patients suffering from aches and pains caused by things like muscular strains and spasms.
Section 1: Anatomy and Function of Muscles and Joints
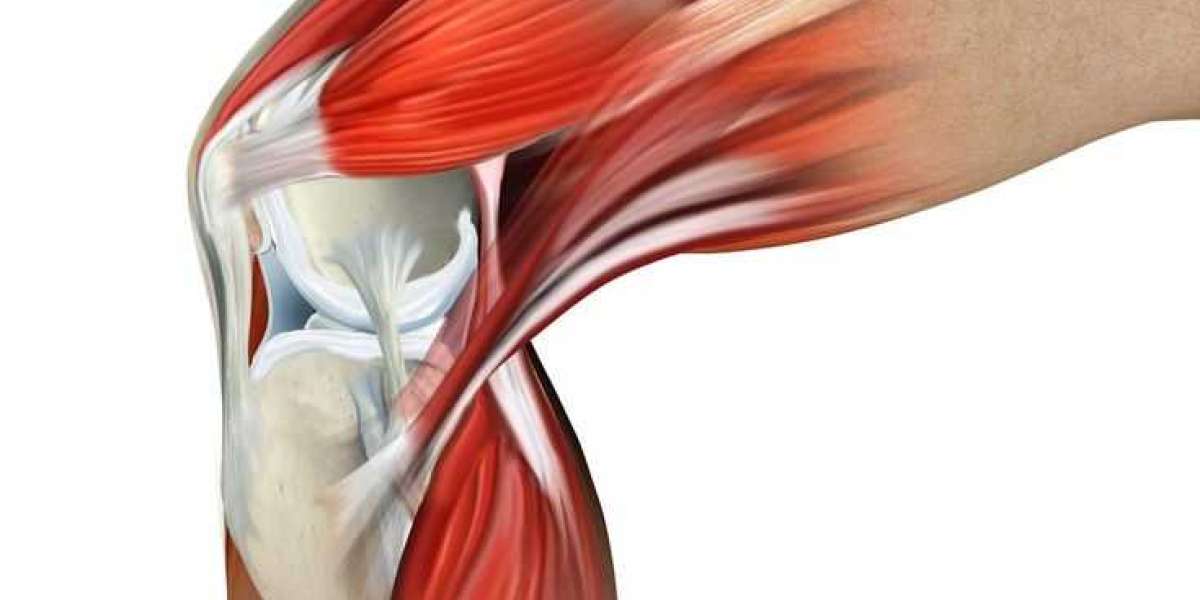
To comprehend muscles and joint pain, it's crucial to first understand the anatomy and function of these essential components of the human body. Muscles are responsible for movement, stability, and posture, while joints facilitate mobility by connecting bones and allowing them to move relative to each other. Exploring the structure and function of muscles and joints provides a foundation for understanding how pain can manifest in these areas.
Section 2: Causes of Muscles and Joint Pain
Muscles and joint pain can arise from a myriad of causes, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Common causes include:
1. Overuse injuries: Repetitive movements or excessive strain on muscles and joints can lead to inflammation and pain.
2. Traumatic injuries: Accidents, falls, and sports injuries can result in muscle strains, ligament sprains, or fractures, causing acute pain.
3. Arthritis: Various forms of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout, can cause chronic inflammation and degeneration of joints, leading to persistent pain.
4. Tendonitis: Inflammation of tendons, often due to overuse or repetitive motions, can result in localized pain and discomfort.
5. Fibromyalgia: A chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tender points.
Understanding the underlying causes of muscles and joint pain is essential for appropriate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Section 3: Symptoms of Muscles and Joint Pain
Muscles and joint pain can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
1. Pain: Ranging from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain, which may be localized or widespread.
2. Stiffness: Difficulty moving a joint or muscle due to stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity.
3. Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the affected joint or muscle.
4. Weakness: Reduced strength and function in the affected area, making everyday tasks challenging.
5. Redness and warmth: Signs of inflammation, particularly in acute or infectious conditions.
Recognizing these symptoms can aid in early detection and prompt management of muscles and joint pain.
Prosoma 350 mg is an anti-inflammatory drug that eases the pain and spasms caused by injuries and musculoskeletal problems. The main ingredient, carisoprodol, helps relax muscles by influencing the transmission of signals in the central nervous system.
Section 4: Diagnosis of Muscles and Joint Pain
Accurate diagnosis is essential for identifying the underlying cause of muscles and joint pain and formulating an effective treatment plan. Diagnosing muscles and joint pain typically involves:
1. Medical history: Gathering information about the onset, duration, and nature of the pain, as well as any predisposing factors or previous injuries.
2. Physical examination: Assessing range of motion, strength, tenderness, and swelling in the affected area.
3. Imaging tests: X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the internal structures of joints and muscles and identify any abnormalities or damage.
4. Laboratory tests: Blood tests may be conducted to rule out underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or infections.
By employing a combination of these diagnostic modalities, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose the cause of muscles and joint pain and tailor treatment accordingly.
Section 5: Treatment Options for Muscles and Joint Pain
The management of muscles and joint pain depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Treatment options may include:
1. Physical therapy: Targeted exercises, stretching, and manual techniques can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion, while also reducing pain and inflammation.
2. Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may provide temporary relief from mild to moderate pain. In severe cases, prescription medications or corticosteroid injections may be necessary.
3. Rest and activity modification: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain or strain can promote healing and prevent further injury.
4. Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat packs or cold compresses to the affected area can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation.
5. Assistive devices: Splints, braces, or orthotic inserts may be recommended to support and stabilize joints, especially in cases of arthritis or injury.
6. Lifestyle modifications: Adopting healthy habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall musculoskeletal health.
7. Alternative therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care may provide symptomatic relief for some individuals with muscles and joint pain.
8. Surgery: In cases of severe joint damage or persistent pain that does not respond to conservative treatments, surgical intervention, such as joint replacement or arthroscopic surgery, may be necessary.
By employing a multidisciplinary approach and personalized treatment plan, healthcare providers can effectively manage muscles and joint pain and improve patients' overall quality of life.
Conclusion:
Muscles and joint pain are common complaints that can significantly impact one's daily functioning and quality of life. By understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options for muscles and joint pain, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively and alleviate pain and discomfort. Through a combination of conservative treatments, lifestyle modifications, and, when necessary, surgical intervention, individuals can regain mobility, reduce pain, and improve their overall musculoskeletal health. With proper care and management, muscles and joint pain need not be a barrier to living a fulfilling and active life.