When it comes to organic chemistry, some compounds stand out for their versatility and reactivity, and Methyl Vinyl Ketone (MVK) is definitely one of them. Known for its strong odor and reactive nature, this small but powerful molecule plays a big role in various chemical processes.
What is Methyl Vinyl Ketone?
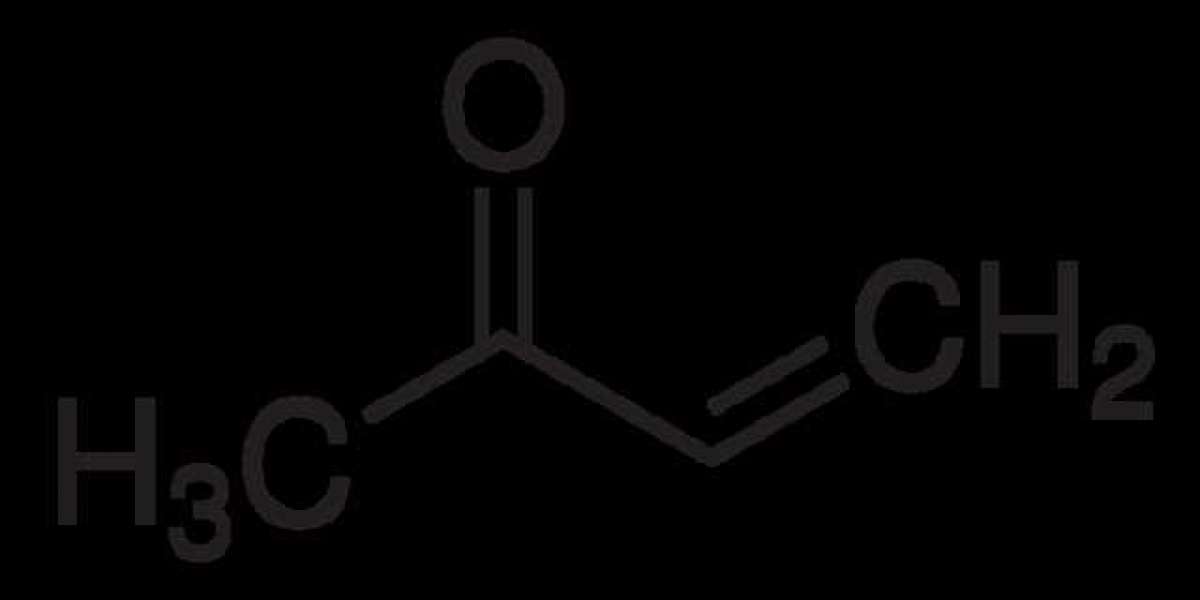
Methyl Vinyl Ketone (MVK), also known as butenone, is an organic compound with the formula CH₃C(O)CH=CH₂. Structurally, it is a combination of a methyl group (-CH₃), a vinyl group (-CH=CH₂), and a carbonyl group (-C=O). This combination gives it unique properties, making it a valuable building block in organic synthesis.
Quick Facts about MVK:
- Molecular Formula: C₄H₆O
- Cas No :- 78-94-4
- Molecular Weight: 70.09 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Boiling Point: 81.4°C
- Density: 0.8407 g/cm³
MVK is a highly reactive, colorless liquid with a pungent, somewhat unpleasant odor. While it may not sound like much at first glance, its reactivity makes it essential in many chemical reactions.
Why is MVK So Special?
What sets Methyl Vinyl Ketone apart from other organic compounds is its ability to undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. The molecule contains both a reactive carbonyl group (C=O) and a double bond (C=C), making it prone to attacks from nucleophiles. This reactivity is exactly what makes MVK so useful in organic synthesis.
One of the most important uses of MVK is in the Robinson Annulation, a reaction used to synthesize ring compounds. This process is vital in the construction of complex organic molecules, particularly in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Whether you're synthesizing new drugs, perfumes, or polymers, MVK plays a crucial role.
Industrial Uses of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
In industry, Methyl Vinyl Ketone is often used as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and agrochemicals. Its ability to react with a wide variety of other chemicals makes it an invaluable asset in the production of complex organic compounds.
However, due to its reactive nature, MVK is also used with caution. It is extremely flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air, so it’s important that it's handled and stored under controlled conditions.
Safety Considerations
Working with Methyl Vinyl Ketone requires proper safety precautions. MVK is classified as toxic and can cause serious harm if inhaled or if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes. Direct exposure to MVK vapors may result in:
- Eye and skin irritation
- Respiratory issues like coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath
- Severe allergic reactions
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respirators, is necessary when handling MVK. It should always be used in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize the risk of exposure.
The Future of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
MVK’s versatility in the lab and in industry continues to make it an important player in the world of organic chemistry. As industries continue to innovate and seek out more efficient ways to produce chemicals, we can expect Methyl Vinyl Ketone to remain at the forefront of chemical research.
While MVK has its risks, with proper handling and safety precautions, it remains a powerful and indispensable tool for chemists and industries worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Methyl Vinyl Ketone (MVK) is a highly reactive compound, used in organic synthesis, particularly in the Robinson Annulation reaction.
- Its reactivity is due to the presence of both a carbonyl group and a vinyl group.
- MVK has industrial applications in pharmaceuticals, plastics, and agrochemicals.
- Due to its toxicity and flammability, MVK must be handled with extreme care.
In the world of organic compounds, Methyl Vinyl Ketone is a small molecule that makes a big impact. Whether you're a chemist in the lab or working in industrial manufacturing, knowing how to handle MVK properly is essential for safety and success